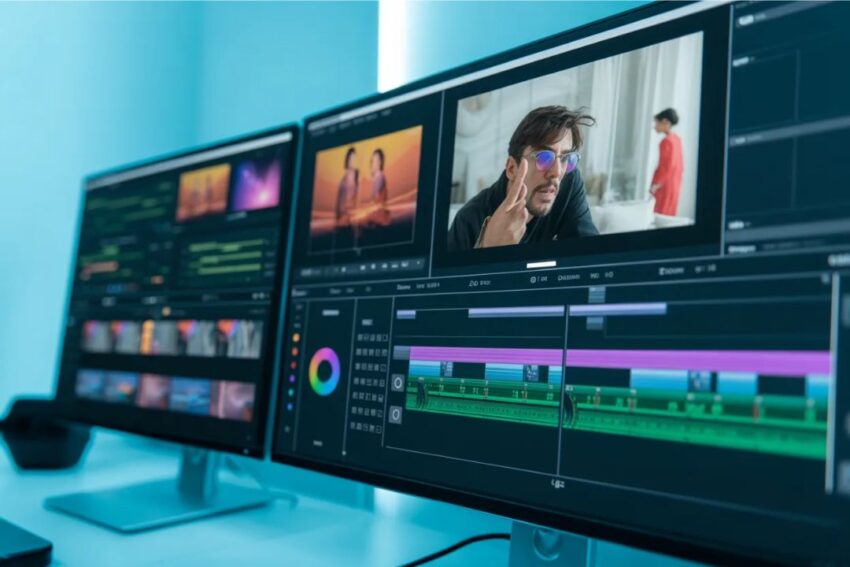
Chapter 1: Understanding Video Editing
1.1 What is Video Editing?
Video editing is the art and process of taking raw footage and transforming it into a finished product that tells a story, conveys a message, or evokes an emotion. It’s more than just cutting clips together—it involves crafting a narrative, balancing audio and visuals, and often adding effects, transitions, or graphics to enhance the viewer’s experience.
Think of video editing like sculpting: the raw footage is the block of marble, and your editing skills carve it into something polished and meaningful. In the digital age, editing is essential for filmmakers, YouTubers, marketers, and even casual content creators.
Key Elements of Video Editing:
- Cutting and trimming: Removing unwanted parts and keeping only the best takes.
- Transitions: Smoothly moving from one clip to another.
- Effects and filters: Adding visual elements to enhance mood or style.
- Audio integration: Syncing sound, adjusting levels, and adding music or voiceovers.
- Color correction and grading: Adjusting colors to create a specific look or feel.
1.2 A Brief History of Video Editing
To truly appreciate modern video editing, it’s worth looking back at how it evolved:
- The Analog Era:
In the early days of film, editing was done manually. Editors physically cut and spliced film strips together using scissors and tape. Each cut had to be precise because mistakes could ruin expensive film reels. - Linear Editing (1970s–1990s):
With the advent of videotape, linear editing allowed editors to rearrange clips sequentially. However, making changes meant re-recording parts of the tape, which was time-consuming. - Non-Linear Editing (1990s–Present):
The digital revolution brought non-linear editing (NLE), where editors can manipulate footage freely without affecting the original file. Software like Adobe Premiere, Final Cut Pro, and Avid Media Composer became industry standards. Non-linear editing dramatically increased efficiency and creativity. - The Modern Era:
Today, video editing has moved beyond desktops. Mobile apps, AI-powered editing, cloud collaboration, and real-time effects have made professional-quality editing accessible to almost anyone.
1.3 Types of Video Editing
Video editing can be broadly categorized into linear and non-linear, but within modern workflows, there are different approaches depending on the type of content:
- Linear Editing:
The traditional method where footage is edited in order, from start to finish. Mostly used in the past for tape-based projects. - Non-Linear Editing (NLE):
Modern editing where clips can be moved, trimmed, and layered in any order. Most software today is NLE-based. - Offline vs. Online Editing:
- Offline editing: Editing a lower-resolution version of footage to save processing power.
- Online editing: Finalizing edits on the high-resolution footage for export.
- Specialized Editing:
- Documentary editing: Focuses on storytelling, pacing, and interviews.
- Music video editing: Fast cuts, synchronization with beats, creative effects.
- Film editing: Balancing narrative, mood, and cinematic techniques.
- Social media editing: Short, engaging, and platform-specific.
1.4 Why Video Editing is Important
Video editing is the bridge between raw footage and a compelling story. Without editing, videos would be unpolished, confusing, or boring. Here’s why it matters:
- Storytelling: A good editor shapes the narrative, controls pacing, and highlights emotions.
- Audience Engagement: Clean cuts, smooth transitions, and interesting effects keep viewers watching.
- Professionalism: Well-edited videos appear polished and credible.
- Branding and Marketing: Consistent editing style helps define a brand’s identity.
- Creativity: Editing allows experimentation with style, rhythm, and visual storytelling.
Chapter 2: Video Editing Software and Tools
2.1 Introduction
Video editing software is the workspace where all your creative ideas come to life. Choosing the right software can make the difference between a frustrating editing experience and a smooth, enjoyable workflow. While all editors share similar goals—cutting, arranging, and enhancing footage—the tools you use can determine how fast, efficient, and creative your work can be.
In this chapter, we’ll explore:
- Free vs. paid software
- Desktop vs. mobile editing apps
- Popular professional software
- Key features to look for
- Tips for selecting the best software for your needs
2.2 Free vs. Paid Video Editing Software
Before diving into specific programs, it’s important to understand the difference between free and paid tools:
Free Software
Free tools are great for beginners or those with tight budgets. They often have:
- Basic editing features: Cutting, trimming, transitions
- Limited effects or export options
- Watermarks in some cases
Popular free software:
- DaVinci Resolve (Free Version): Professional-grade color grading and editing for free.
- HitFilm Express: Good for VFX-heavy projects.
- iMovie: Mac users can start simple projects easily.
- Shotcut: Open-source, cross-platform, and beginner-friendly.
Paid Software
Paid tools usually include:
- Advanced features like multi-cam editing, 3D effects, and motion graphics
- Better export options and higher resolutions
- Professional support and updates
Popular paid software:
- Adobe Premiere Pro: Industry standard, integrates with other Adobe apps.
- Final Cut Pro (Mac only): Optimized for Apple hardware, fast rendering.
- Sony Vegas Pro: Intuitive interface, strong audio tools.
- DaVinci Resolve Studio: Paid version with advanced color grading and effects.
2.3 Popular Video Editing Software in Detail
2.3.1 Adobe Premiere Pro
- Platform: Windows, Mac
- Best for: Professional video editing, YouTube, marketing videos
- Features: Multi-camera editing, Lumetri color tools, motion graphics integration, team collaboration
- Pros: Highly versatile, industry-standard, integrates with After Effects and Photoshop
- Cons: Subscription-based, steep learning curve
2.3.2 Final Cut Pro
- Platform: Mac only
- Best for: Mac users wanting fast, high-quality editing
- Features: Magnetic timeline, advanced color grading, 360° video support, motion graphics
- Pros: Optimized for Mac, fast rendering, one-time purchase
- Cons: Mac-only, learning curve for beginners
2.3.3 DaVinci Resolve
- Platform: Windows, Mac, Linux
- Best for: Color grading, professional editing, free or paid options
- Features: Color correction, Fusion for VFX, Fairlight for audio, multi-cam editing
- Pros: Free version is powerful, excellent color tools
- Cons: Resource-intensive, may be overwhelming for beginners
2.3.4 iMovie
- Platform: Mac, iPhone, iPad
- Best for: Beginners and casual editors
- Features: Simple drag-and-drop editing, basic transitions and effects, easy audio integration
- Pros: Free, beginner-friendly
- Cons: Limited advanced features, Mac-only
2.3.5 HitFilm Express
- Platform: Windows, Mac
- Best for: VFX-heavy projects and YouTube creators
- Features: Compositing tools, built-in visual effects, multi-track editing
- Pros: Free, strong effects library
FAQs: Video Editing Software and Tools
1. What is the best video editing software for beginners?
For beginners, free and simple tools are ideal. iMovie (Mac), Shotcut, or CapCut (mobile) are excellent starting points because they are user-friendly and don’t overwhelm you with advanced features.
2. Do I need paid software to edit videos professionally?
Not necessarily. Free software like DaVinci Resolve offers professional-grade features, including color correction, audio tools, and multi-cam editing. Paid software like Adobe Premiere Pro or Final Cut Pro can streamline workflow and offer more advanced tools, but beginners can start free and upgrade as needed.
3. Can I edit videos on my phone?
Yes! Mobile apps like CapCut, Kinemaster, InShot, and LumaFusion allow you to create polished videos directly on your smartphone or tablet, making them ideal for social media content.
4. Which software is best for YouTube videos?
It depends on your skill level:
- Beginner: CapCut, iMovie
- Intermediate: DaVinci Resolve
- Advanced/Professional: Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro
5. Do I need a powerful computer to edit videos?
For basic editing (trimming, simple transitions), almost any modern computer will work. For advanced software like Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, or high-resolution 4K/8K video projects, a powerful processor, lots of RAM, and a strong GPU are recommended.
Conclusion
Choosing the right video editing software is one of the most important decisions for any editor. The tool you use influences your workflow, efficiency, and the quality of your final product.
Key takeaways:
- Free software is perfect for beginners and learning, but paid options unlock professional-grade features.
- Desktop software provides the most control and advanced editing tools.
- Mobile apps are convenient and surprisingly powerful for social media content.
- Consider your skill level, budget, platform, and content goals when selecting software.
- Experimenting with different tools will help you find what works best for your style and workflow.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each editing tool, you can focus more on creativity, storytelling, and producing polished videos, rather than struggling with technical issues.
